DOT: Final Rule on Air Taxi Pilot Training, Operations Coming Soon
At the Honeywell Advanced Air Mobility Summit in Washington, D.C., stakeholders clamor for regulatory clarity.
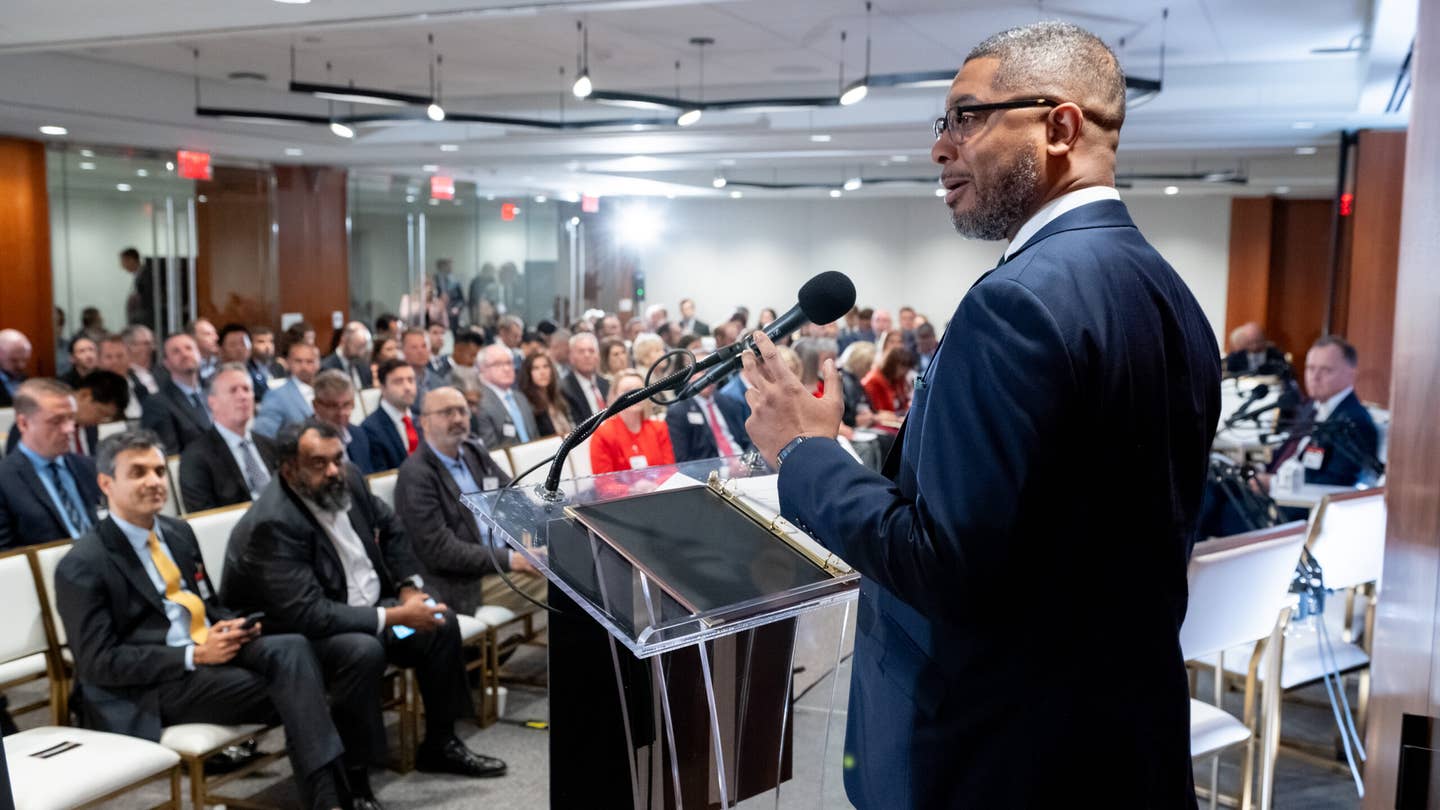

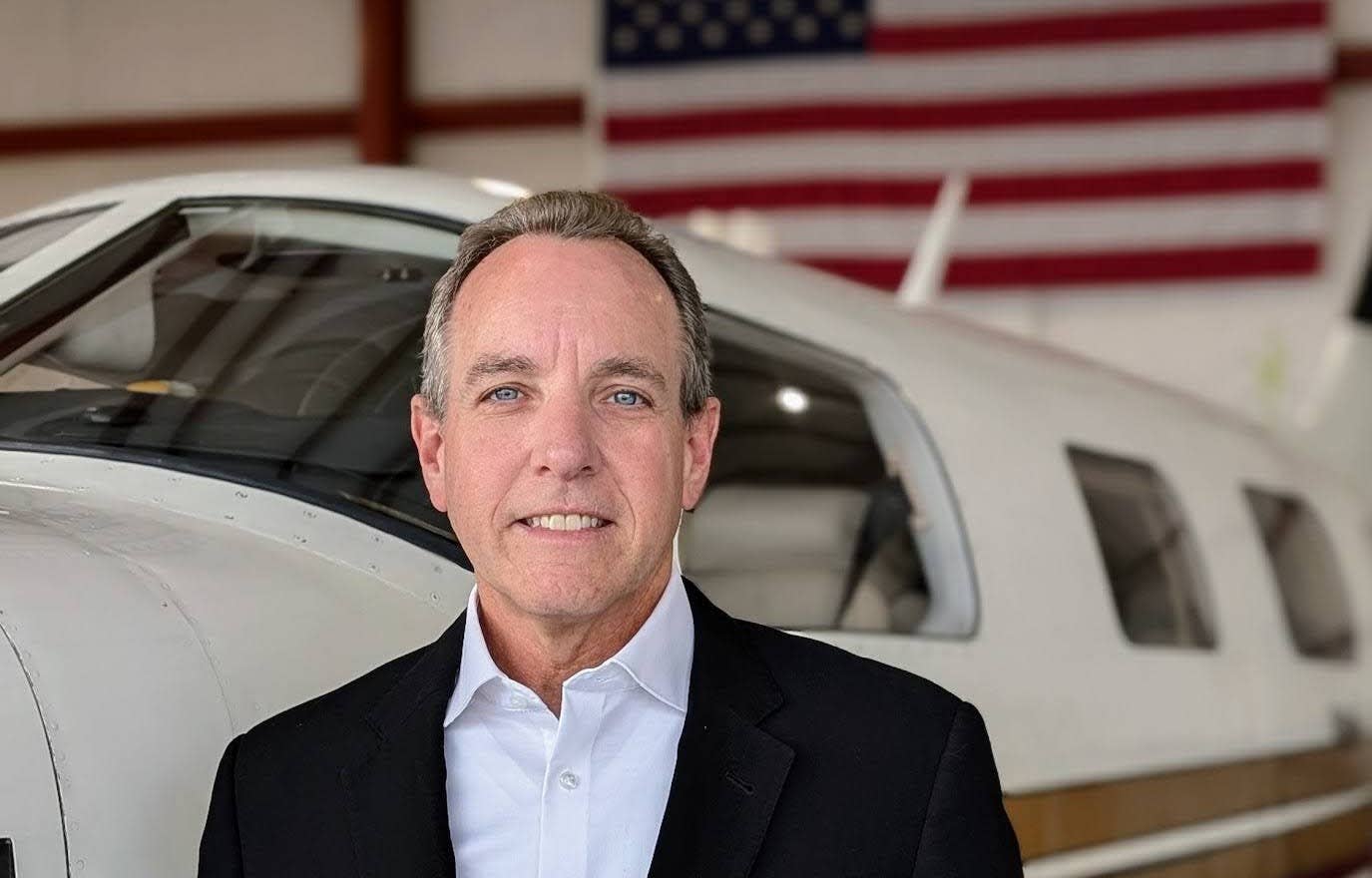
Christopher Coes, acting undersecretary of transportation for policy for the U.S. Department of Transportation, delivers a keynote at Honeywell’s third annual AAM Summit in Washington, D.C., on Thursday. [Courtesy: Honeywell]
Correction: This story was updated on Sept. 23, 2024.
WASHINGTON, D.C.—Within the next month, the FAA will release a final rule outlining pilot certification and initial operations for electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) air taxis and other powered-lift aircraft, a U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) official said Thursday.
At Honeywell’s third annual Advanced Ait Mobility (AAM) Summit in Washington, D.C., Christopher Coes, acting undersecretary of transportation for policy within the DOT, said a highly anticipated special federal aviation regulation (SFAR) defining the rules will be published in the next few weeks.
“The department has a final rule for our powered-lift operations, and we expect that that will be published in the next month,” Coes said. “And I think you will see it is quite responsive to the industry’s comments.”
Industry Raises Concerns
The FAA published a notice of proposed rulemaking (NPRM) for the powered-lift SFAR in June 2023. The rule would set alternative training and eligibility requirements for certifying powered-lift pilots as well as create operational rules for passenger and cargo transport.
But the document was decried by a collective of stakeholders, spearheaded by the General Aviation Manufacturers Association (GAMA), who took issue with many of the agency’s proposals.
Namely, industry groups believe powered-lift training courses should credit existing rotorcraft and airplane category certificates, and pilots should be able to add a powered-lift rating directly to those permissions. They urged the FAA to lower the threshold for powered-lift flight hours, remove a requirement that limits training to dual control aircraft, and allow more training in simulators.
The groups also argue that performance-based—rather than prescriptive—rules should be used for powered-lift flight, such as by applying airplane and rotorcraft rules as appropriate rather than creating a new category of operations.
Kristie Greco Johnson, senior vice president of government affairs for the National Business Aviation Association (NBAA), said Thursday that members are seeking a “practical pathway” to AAM integration. And the SFAR could be that pathway.
“AAM isn’t a future Jetsons concept. It is actually happening right now in our airspace.”
—Kristie Greco Johnson, senior vice president of government affairs, NBAA
“AAM isn’t a future Jetsons concept,” Johnson said. “It is actually happening right now in our airspace.”
Amanda Joyner, managing director of government affairs for GAMA, agreed with Johnson and said members are hopeful that the SFAR will help them to get their products on the market quickly. Eventually, investment into AAM manufacturers will dry up if the firms are unable to demonstrate a product, so a final rule could help them begin to turn a profit.
What It Means
The deadline for a powered-lift SFAR is December 16, as mandated by the FAA Reauthorization Act of 2024 signed into law on May 16—a provision that was lauded by industry organizations, private companies, and lawmakers alike.
The FAA earlier this week missed the bill’s September 16 deadline to issue a NPRM for beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) drone flight. But Andrew Miller, a staffer on the Senate Commerce Minority Committee, and Alexander Simpson, a staffer on that chamber’s majority counterpart, said they are confident the FAA will meet the SFAR timeframe. Hunter Presti, a staffer on the House Majority Transportation Committee, is optimistic but believes it will be tight.
According to Simpson, should the agency miss its deadline, existing standards and regulations for rotorcraft and fixed-wing aircraft would apply to powered-lift models.
Coes said his office is simultaneously developing a U.S. national strategy to safely integrate AAM operations alongside conventional aircraft. That plan has been in the works for over a year and is under department review.
The initiative will require an interagency review and final briefing to Congress, “but I am confident that this will be a set of documents that can be championed by the industry, by academia, by labor, our state and local partners, as well as Congress,” Coes said.
Coes added that his team is working with the International Civil Aviation Organization’s AAM study group to harmonize international consensus on AAM standards, practices, and procedures. The goal, he said, is to ensure the U.S. takes the reins on those provisions.
Conference attendees including Coes hope the FAA and other federal agencies will be able to use the Los Angeles Olympic Games in 2028 as a showcase for AAM technology. The event could also serve as a proving ground for the integration of AAM aircraft with other transportation systems.
In support of that effort, the FAA last year released its Innovate28 blueprint for air taxi integration. Earlier this year, the agency proposed comprehensive certification criteria for AAM aircraft, laying the groundwork to get them approved to fly.
But there is still a long way to go, and the powered-lift SFAR—whenever it is released—will be a key part of the process.
Like this story? We think you'll also like the Future of FLYING newsletter sent every Thursday afternoon. Sign up now.

Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest FLYING stories delivered directly to your inbox